# Customize Bootstrap with CSS Variables
In this chapter, we will explore how to customize Bootstrap using CSS variables. We'll learn how to create a custom
theme by adding variables to the :root selector, enabling us to easily apply our styles across our CSS files. We will
also modify some of Bootstrap's global settings, incorporate Bootstrap components styled with our custom theme, and even
build a custom component from scratch.
# Prerequisites
Before starting, ensure you have the following:
- Clone the start project: Obtain the project files from the GitHub repository (opens new window).
- Install live-server: Use npm to install the live-server globally.
npm install -g live-serverCopied!1 - Run live-server: Start the development server with the command below.
npm run watchCopied!1
# File Structure
The project is organized as follows:
📂css_bootstrap_demo_project/ ├── 📂src/ │ ├── 📂css/ │ │ ├── 📂bootstrap/ │ │ │ └── 📄bootstrap5.3.8.min.css │ │ └── 📂components/ │ │ ├── 📄alert.css │ │ ├── 📄button.css │ │ ├── 📄callout.css │ │ ├── 📄content.css │ │ ├── 📄main.css │ │ └── 📄root.css │ ├── 📂js/ │ │ └── 📄bootstrap5.3.8.min.js │ ├── 📄index.html └── 📄package.json └── 📄README.mdCopied!
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
All the necessary files for this demonstration are located within the src directory. The basic project setup is
already completed, and our focus will be on customizing the Bootstrap framework.
- The
index.htmlfile serves as the main entry point of the project. It includes several components that we will style using our custom theme. - The page links to
main.css, where we will import all our CSS files, and tobootstrap5.3.8.min.jsfor Bootstrap's JavaScript functionality.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Bootstrap Custom Variables Demo</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/main.css"> </head> <body> ... <script src="js/bootstrap5.3.8.min.js"></script> </body> </html>Copied!
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# Create a Custom Theme
Let's begin by establishing a custom theme for our project. We will utilize the following color palette for this example:
#f04b20
#009cab
#f0cf1f
#546363
NAMING CONVENTION
- We will follow the naming convention
tm-<color-name>for our custom theme colors. You are free to use any naming scheme, provided it does not conflict with existing Bootstrap class names. - Using suffixes like
primary,secondary, andtertiaryfacilitates easy switching between different themes in the future. - The suffix
textwill be used for text and background colors within our theme.
# Add Theme Colors to the :root Selector
Now, let's create CSS variables for our chosen colors and add them to the :root selector within the root.css file.
Because root.css is imported after Bootstrap's CSS, our custom theme colors will override Bootstrap's defaults. This
allows us to introduce custom properties that we can then utilize throughout our CSS.
TIP
- We have created a simple web tool to help you generate various shades of a color.
- Visit https://css-shades.netlify.app/ (opens new window):
- Click on the color picker to select your desired color. (Use the double arrow in the bottom right to switch between RGB, HSL, and HEX formats).
- Modify the color name as needed.
- Copy the generated CSS custom properties and paste them into the
:rootselector in yourroot.cssfile. - Shade 400 typically represents the base color.
- Utilize the web tool to generate custom properties for our color palette:
- Base color:
#f04b20, Color name:tm-primary - Base color:
#009cab, Color name:tm-secondary - Base color:
#f0cf1f, Color name:tm-tertiary - Base color:
#546363, Color name:tm-slate - Open the file src/css/root.css and insert the generated custom properties within a
:rootselector.
:root { --tm-primary-25: #feede9; --tm-primary-50: #fcdbd2; --tm-primary-100: #f9b7a6; --tm-primary-200: #f69379; --tm-primary-300: #f36f4d; --tm-primary-400: #f04b20; --tm-primary-500: #d8441d; --tm-primary-600: #c03c1a; --tm-primary-700: #a83516; --tm-primary-800: #902d13; --tm-primary-900: #782610; --tm-primary-950: #601e0d; --tm-secondary-25: #e6f5f7; --tm-secondary-50: #ccebee; --tm-secondary-100: #99d7dd; --tm-secondary-200: #66c4cd; --tm-secondary-300: #33b0bc; --tm-secondary-400: #009cab; --tm-secondary-500: #008c9a; --tm-secondary-600: #007d89; --tm-secondary-700: #006d78; --tm-secondary-800: #005e67; --tm-secondary-900: #004e56; --tm-secondary-950: #003e44; --tm-tertiary-25: #fefae9; --tm-tertiary-50: #fcf5d2; --tm-tertiary-100: #f9eca5; --tm-tertiary-200: #f6e279; --tm-tertiary-300: #f3d94c; --tm-tertiary-400: #f0cf1f; --tm-tertiary-500: #d8ba1c; --tm-tertiary-600: #c0a619; --tm-tertiary-700: #a89116; --tm-tertiary-800: #907c13; --tm-tertiary-900: #786810; --tm-tertiary-950: #60530c; --tm-text-25: #eeefef; --tm-text-50: #dde0e0; --tm-text-100: #bbc1c1; --tm-text-200: #98a1a1; --tm-text-300: #768282; --tm-text-400: #546363; --tm-text-500: #4c5959; --tm-text-600: #434f4f; --tm-text-700: #3b4545; --tm-text-800: #323b3b; --tm-text-900: #2a3232; }Copied!
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
# Global Settings
# Modify the :root Selector
- To inspect the contents of Bootstrap's
:rootselector, you can open thebootstrap5.3.8.min.cssfile and search for:root. - Since this file is minified, it is not easily readable. Alternatively, you can view the original
bootstrap5.3.8.cssfile in your browser by navigating to: https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/bootstrap/5.3.8/css/bootstrap.css (opens new window).
- The
:rootselector in Bootstrap contains global settings such as:--bs-font-sans-serif: Defines the default sans-serif font family.--bs-body-color: Sets the default text color for the<body>.--bs-body-bg: Sets the default background color for the<body>.--bs-border-radius: Defines the standard border-radius applied to various elements.- ...
- Let's override these four settings in our
root.cssfile.
:root { --bs-font-sans-serif: "Inter", sans-serif; --bs-body-color: var(--tm-text-700); --bs-body-bg: var(--tm-text-25); --bs-border-radius: 0; --tm-primary-25: #feede9; ... }Copied!
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# Customize Other Elements
We can further customize the styling by modifying properties of standard HTML tags within our project. This can be
accomplished in the content.css file.
- Open the file src/css/content.css and apply the following changes to heading tags:
- Set the color of all heading tags (h1 to h6) to
#007d89and the font-size to2rem. - For the
h2tag, add a top and bottom padding of1remand set the font-size to1.5rem. - Add a
::beforepseudo-element to theh2tag with the content"★ ".
- Set the color of all heading tags (h1 to h6) to
h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, h6 { color: var(--tm-secondary-600); font-size: 2rem; } h2 { padding: 1rem 0; font-size: 1.5rem; &::before { content: "★ "; } }Copied!
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# Components
To identify the CSS variables used within Bootstrap components, the most effective method is to inspect the source code using your browser's developer tools. We'll start by examining a default Bootstrap component to understand which CSS variables are in use, which will guide our customization efforts.
# Alert Components
- Inspect the primary alert component using your browser's developer tools to see the associated CSS variables.
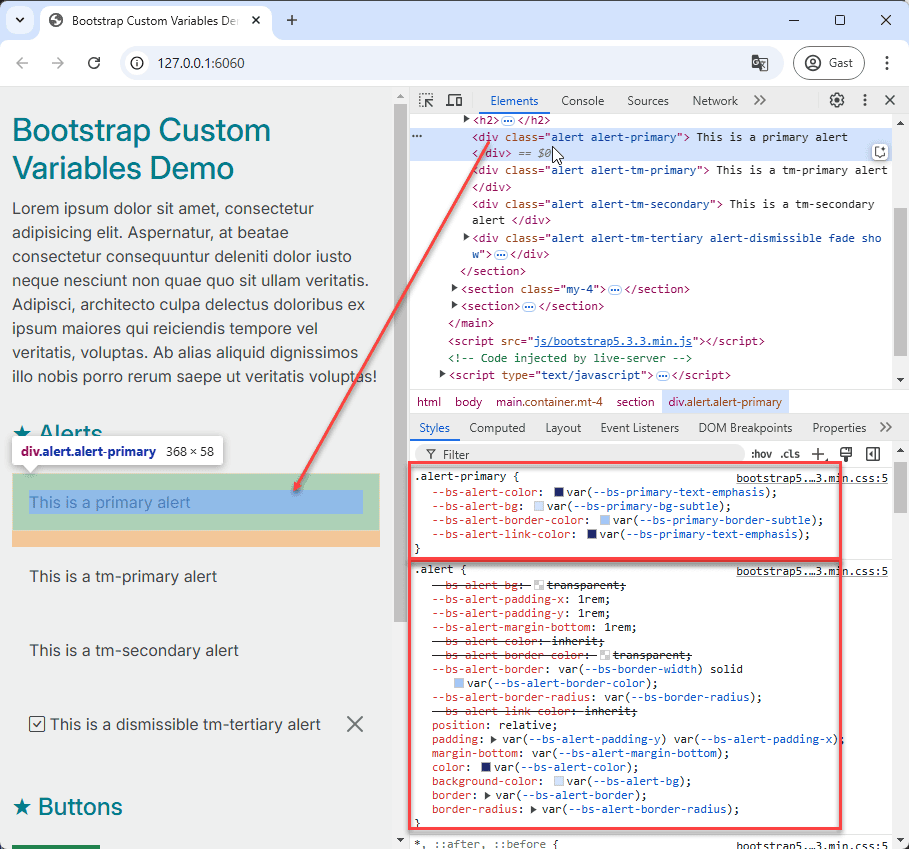
- Open the file src/css/components/alert.css.
- Copy the entire
.alert-primaryclass definition from the browser's developer tools and paste it intoalert.css. - Rename the class to
.alert-tm-primaryand update the values of the--bs-alert-color,--bs-alert-bg,--bs-alert-border-color, and--bs-alert-link-colorproperties using shades from ourtm-primarycolor palette. - Repeat this process for the
.alert-tm-secondaryand.alert-tm-tertiaryclasses.
.alert-tm-primary { --bs-alert-color: var(--tm-primary-600); --bs-alert-bg: var(--tm-primary-50); --bs-alert-border-color: var(--tm-primary-200); --bs-alert-link-color: var(--tm-primary-600); } .alert-tm-secondary { --bs-alert-color: var(--tm-secondary-600); --bs-alert-bg: var(--tm-secondary-50); --bs-alert-border-color: var(--tm-secondary-200); --bs-alert-link-color: var(--tm-secondary-600); } .alert-tm-tertiary { --bs-alert-color: var(--tm-tertiary-700); --bs-alert-bg: var(--tm-tertiary-50); --bs-alert-border-color: var(--tm-tertiary-400); --bs-alert-link-color: var(--tm-tertiary-700); }Copied!
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
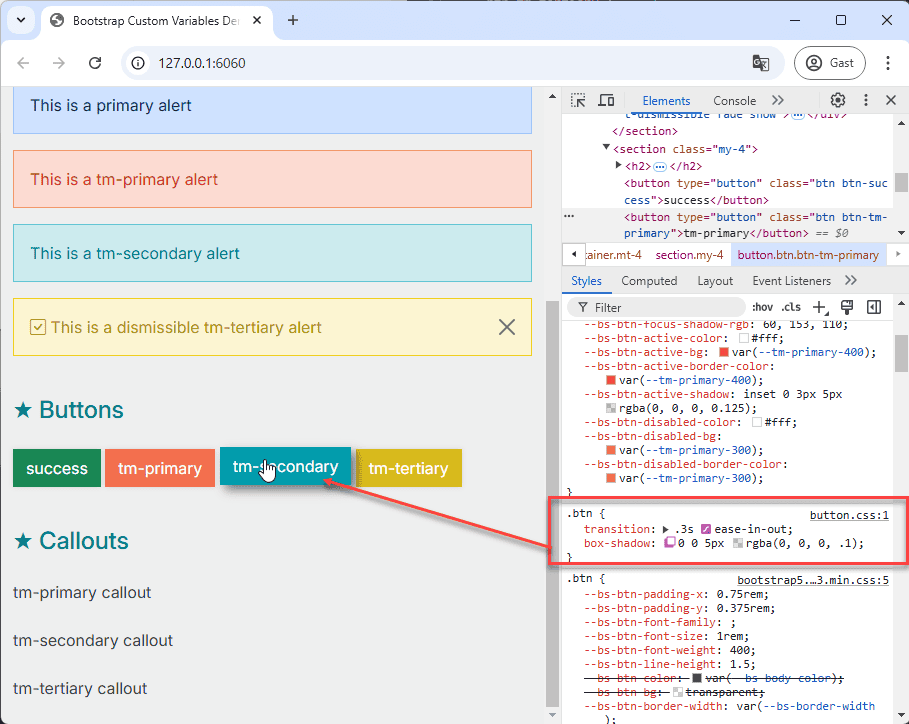
# Button Components
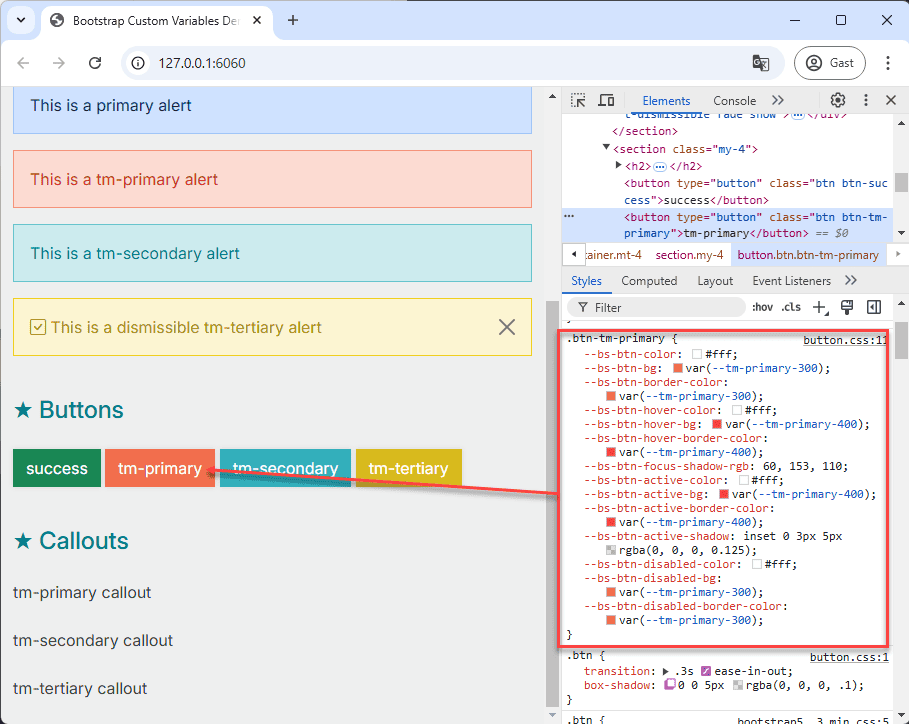
- Inspect the primary button component using your browser's developer tools to identify the relevant CSS variables.
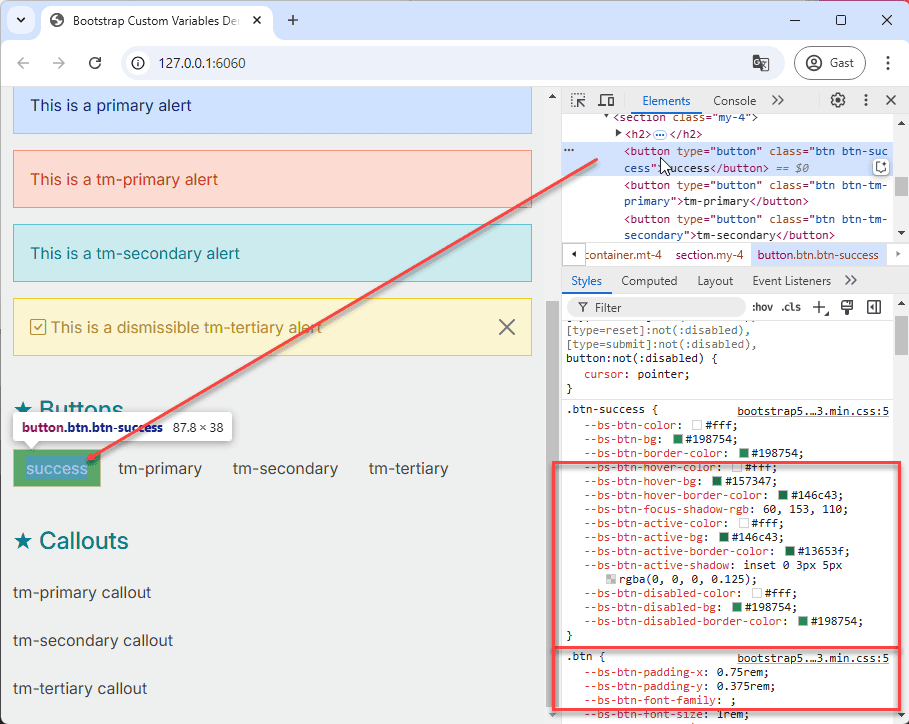
- Open the file src/css/components/button.css.
- Copy the complete
.btn-successclass definition from the browser's developer tools and paste it intobutton.css. - Rename the class to
.btn-tm-primaryand update all the CSS variable values using shades from thetm-primarycolor palette. - Repeat this for the
.btn-tm-secondaryand.btn-tm-tertiaryclasses.
.btn-tm-primary { --bs-btn-color: #fff; --bs-btn-bg: var(--tm-primary-300); --bs-btn-border-color: var(--tm-primary-300); --bs-btn-hover-color: #fff; --bs-btn-hover-bg: var(--tm-primary-400); --bs-btn-hover-border-color: var(--tm-primary-400); --bs-btn-focus-shadow-rgb: 60, 153, 110; --bs-btn-active-color: #fff; --bs-btn-active-bg: var(--tm-primary-400); --bs-btn-active-border-color: var(--tm-primary-400); --bs-btn-active-shadow: inset 0 3px 5px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.125); --bs-btn-disabled-color: #fff; --bs-btn-disabled-bg: var(--tm-primary-300); --bs-btn-disabled-border-color: var(--tm-primary-300); } .btn-tm-secondary { --bs-btn-color: #fff; --bs-btn-bg: var(--tm-secondary-300); --bs-btn-border-color: var(--tm-secondary-300); --bs-btn-hover-color: #fff; --bs-btn-hover-bg: var(--tm-secondary-400); --bs-btn-hover-border-color: var(--tm-secondary-400); --bs-btn-focus-shadow-rgb: 60, 153, 110; --bs-btn-active-color: #fff; --bs-btn-active-bg: var(--tm-secondary-400); --bs-btn-active-border-color: var(--tm-secondary-400); --bs-btn-active-shadow: inset 0 3px 5px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.125); --bs-btn-disabled-color: #fff; --bs-btn-disabled-bg: var(--tm-secondary-300); --bs-btn-disabled-border-color: var(--tm-secondary-300); } .btn-tm-tertiary { --bs-btn-color: #fff; --bs-btn-bg: var(--tm-tertiary-500); --bs-btn-border-color: var(--tm-tertiary-500); --bs-btn-hover-color: #fff; --bs-btn-hover-bg: var(--tm-tertiary-600); --bs-btn-hover-border-color: var(--tm-tertiary-600); --bs-btn-focus-shadow-rgb: 60, 153, 110; --bs-btn-active-color: #fff; --bs-btn-active-bg: var(--tm-tertiary-600); --bs-btn-active-border-color: var(--tm-tertiary-600); --bs-btn-active-shadow: inset 0 3px 5px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.125); --bs-btn-disabled-color: #fff; --bs-btn-disabled-bg: var(--tm-tertiary-500); --bs-btn-disabled-border-color: var(--tm-tertiary-500); }Copied!
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
The base .btn class can be further enhanced by adding custom properties. Let's introduce an animation and a box-shadow
to the button's :hover state.
.btn { box-shadow: 0 0 5px rgba(0, 0, 0, .1); transition: .3s ease-in-out; &:hover { box-shadow: 5px 5px 10px rgba(0, 0, 0, .5); transform: translateY(-2px); } } .btn-tm-primary { ... } .btn-tm-secondary { ... } .btn-tm-tertiary { ... }Copied!
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
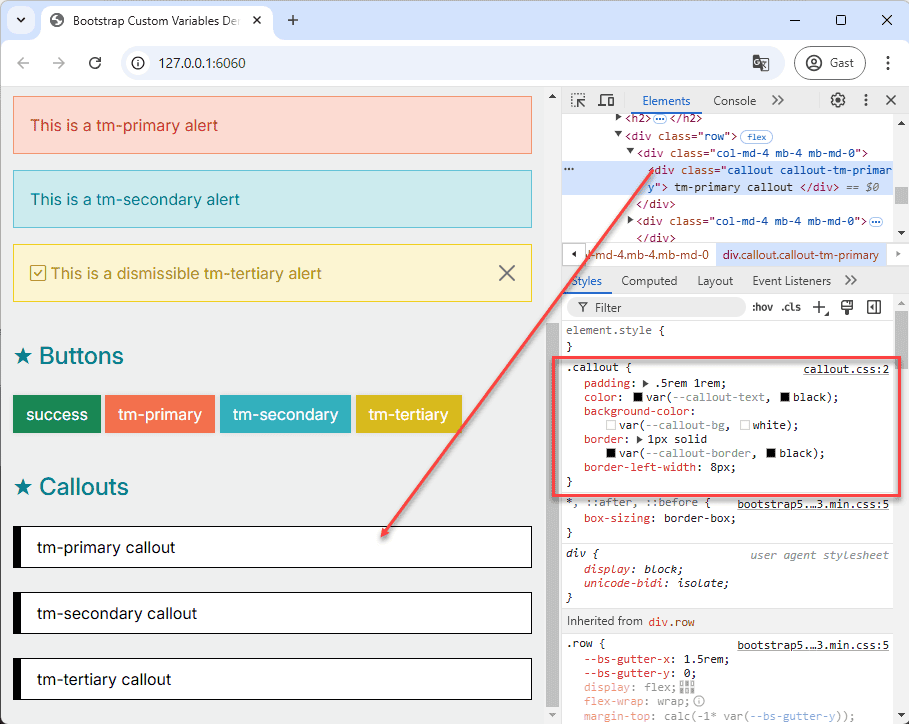
# Create a Custom callout Component
Now, let's create a custom component, the callout, which is not included in the Bootstrap framework but will be styled
with our custom theme. We'll follow a similar structure to Bootstrap's components:
- A base class
.calloutto define general properties. - Modifier classes
.callout-tm-primary,.callout-tm-secondary, and.callout-tm-tertiaryfor applying different theme colors.
For this custom component, we'll use a slightly different approach:
- The base class
.calloutwill have custom properties with default fallback values. - The modifier classes will override these default values to apply our custom theme colors.
# Create the Base Class .callout
- Open the file src/css/components/callout.css.
- Add the base class
.calloutwith the following properties:
.callout { padding: .5rem 1rem; color: var(--callout-text, black); background-color: var(--callout-bg, white); border: 1px solid var(--callout-border, black); border-left-width: 8px; }Copied!
2
3
4
5
6
7
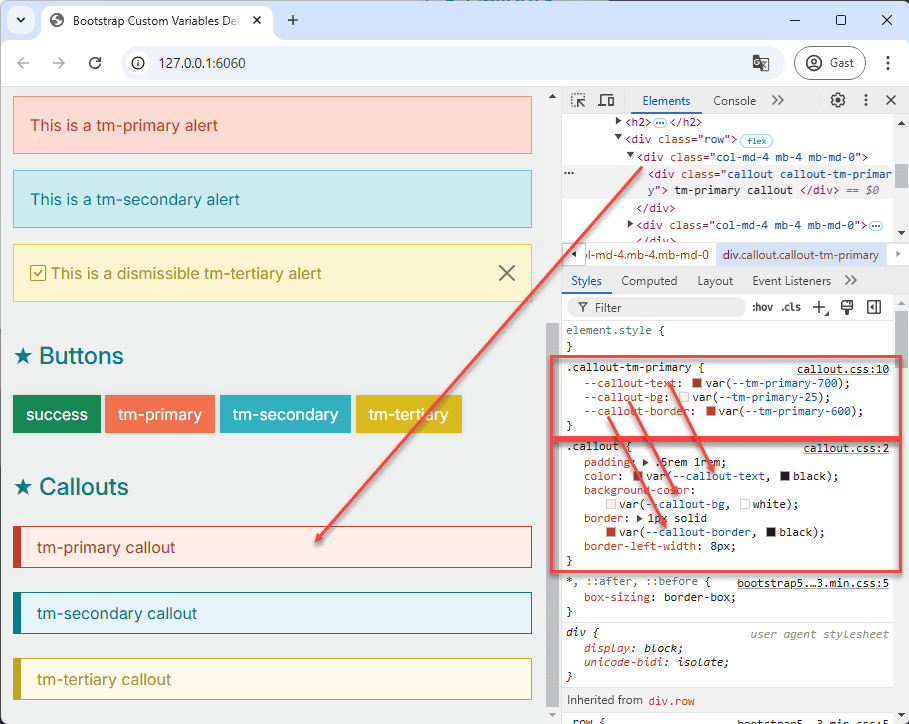
# Create the Modifier Classes
The next step is to add the custom properties to the modifier classes: .callout-tm-primary, .callout-tm-secondary,
and .callout-tm-tertiary.
- Add the modifier classes
.callout-tm-primary,.callout-tm-secondary, and.callout-tm-tertiarywith the following properties:
.callout { ... } .callout-tm-primary { --callout-text: var(--tm-primary-700); --callout-bg: var(--tm-primary-25); --callout-border: var(--tm-primary-600); } .callout-tm-secondary { --callout-text: var(--tm-secondary-700); --callout-bg: var(--tm-secondary-25); --callout-border: var(--tm-secondary-600); } .callout-tm-tertiary { --callout-text: var(--tm-tertiary-700); --callout-bg: var(--tm-tertiary-25); --callout-border: var(--tm-tertiary-600); }Copied!
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
# Conclusion
By leveraging CSS variables, we've successfully customized Bootstrap to match our desired theme. This approach allows for a more maintainable and scalable styling system. We've seen how to override Bootstrap's default variables, style existing components, and even create new components that seamlessly integrate with our custom theme. This methodology is crucial for building consistent and branded web applications efficiently.